Multidisciplinary Skills
collaboration
creative problem-solving
critical thinking
data analysis
design research
design software
graphic representation
fabrication
facilitation
illustration
information design
interviews
leadership
listening
observation
personas
programming
project management
problem framing
rapid prototyping
semiotics
sketching
technical skills
typography
experience mapping
user stories
user testing
verbal and written communication
visual synthesis
visualization
Share
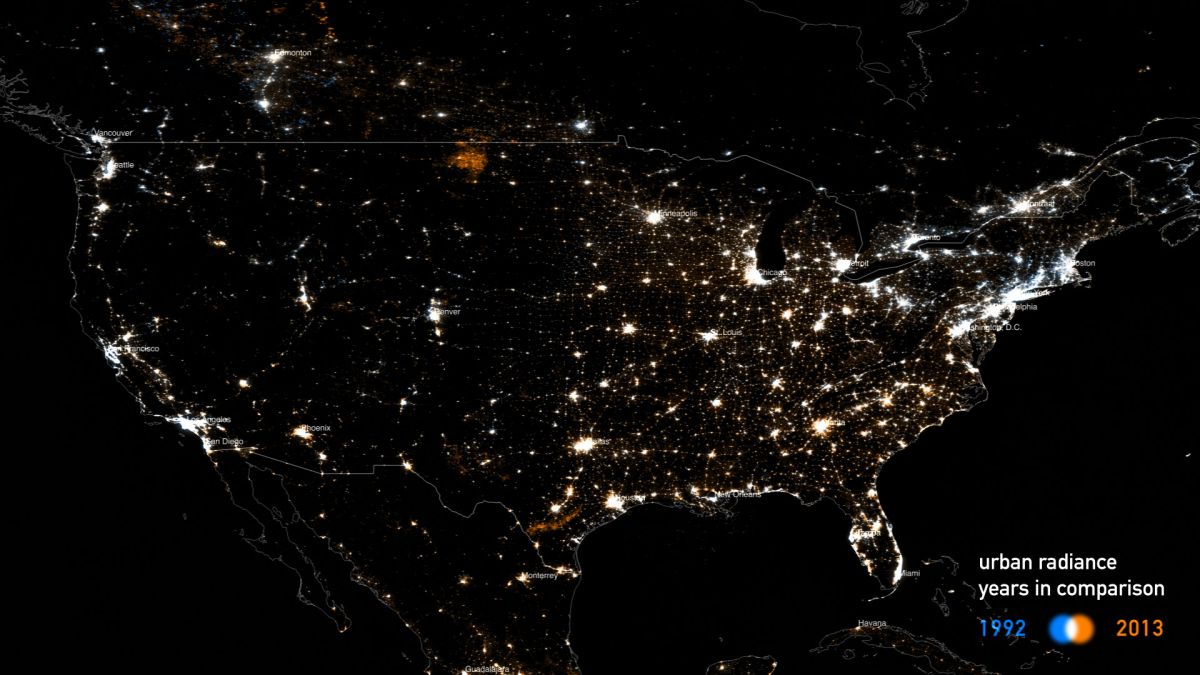
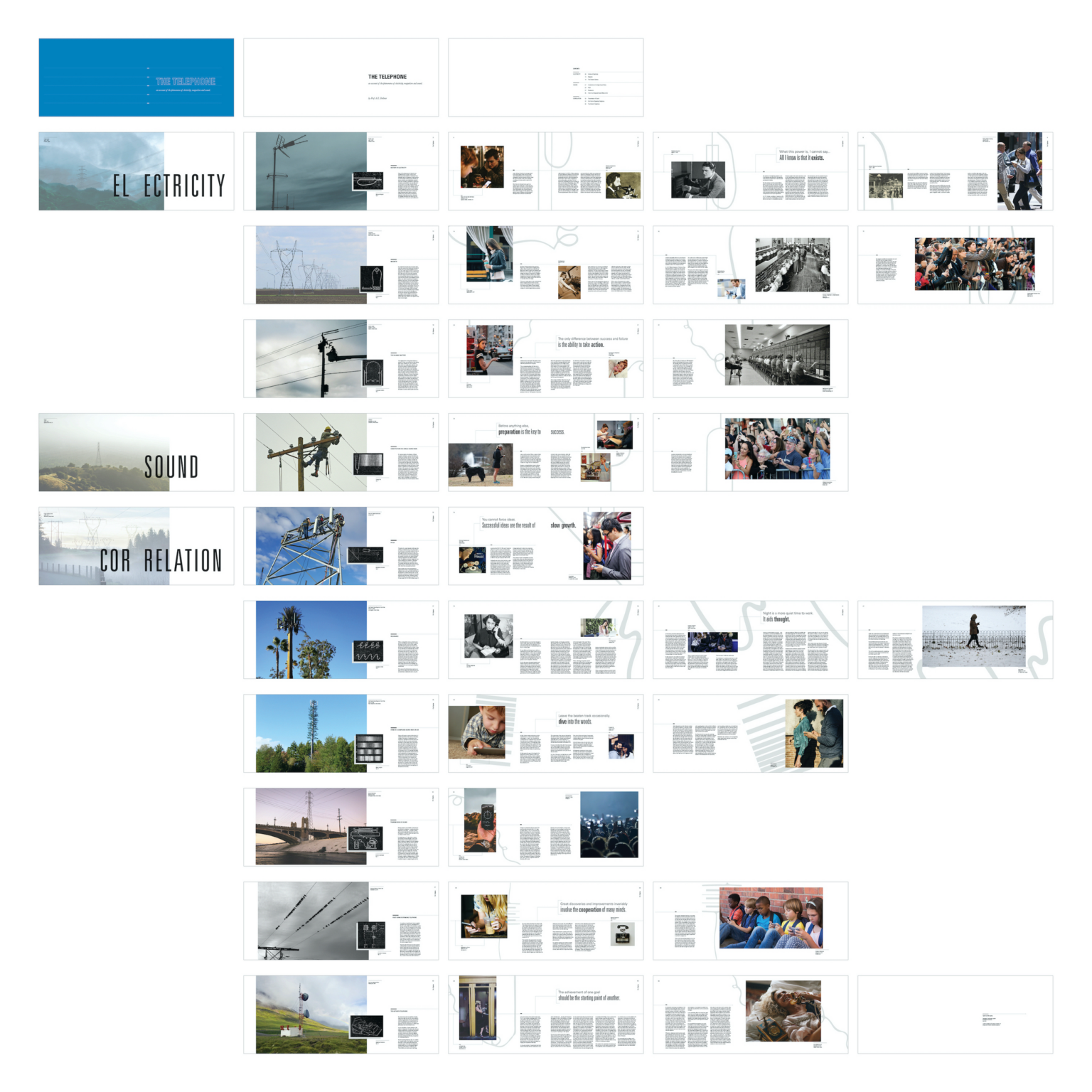
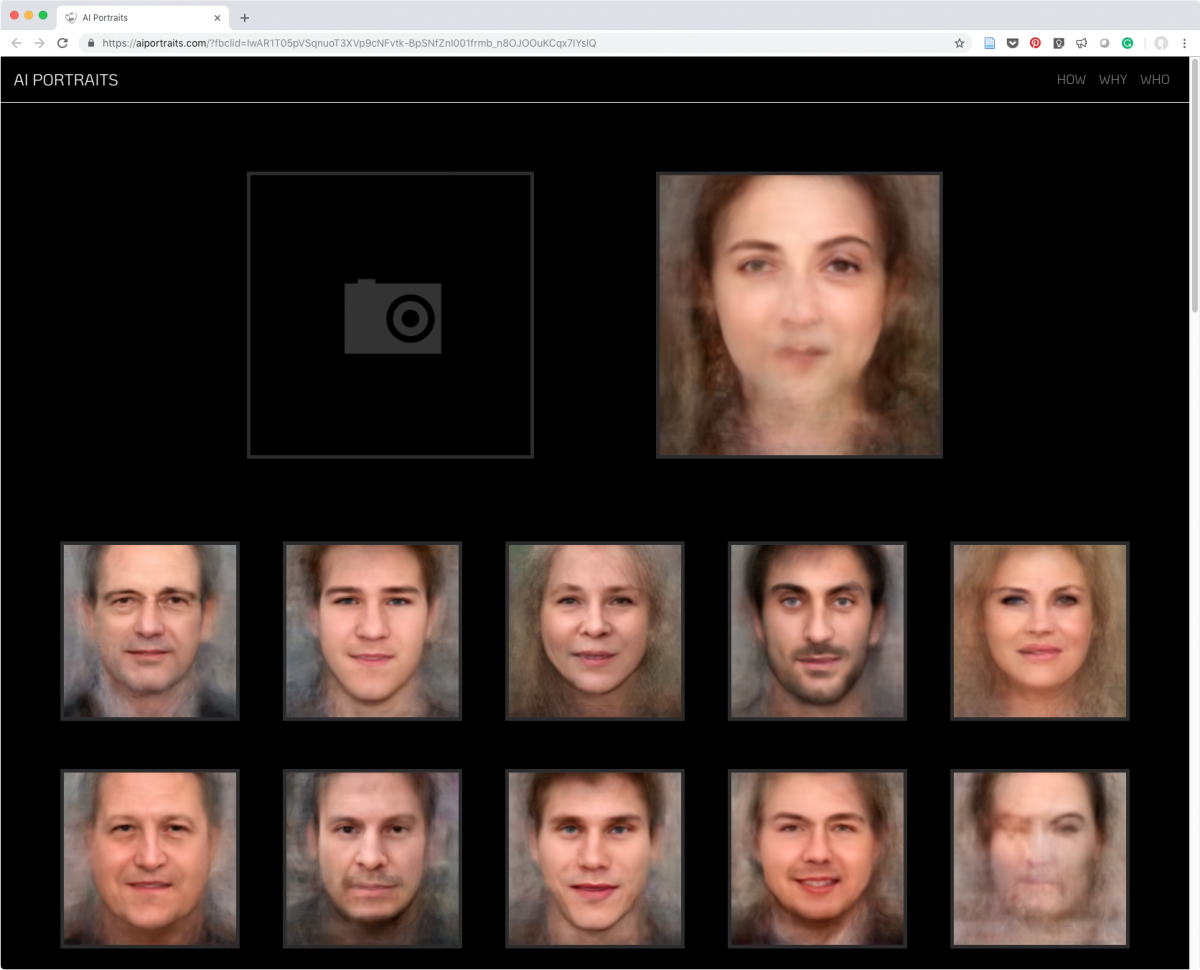
Designers propose alternative futures and create new choices using principles and processes to create, compose, and construct meaning in diverse knowledge fields. Designers seek a broad understanding of principles and systems of perception, communication, and action. Graphic designers exploit rules of visual composition, form, and pattern to construct narratives or to command attention. Their work often has a persuasive intent. Information designers visualize concepts and data to enhance human understanding of complex and vital knowledge. Their work often has an enlightening or instructive intent.
Design Learning Outcomes
- Apply iterative design processes to create, revise, evaluate, and develop effective prototypes and innovative solutions.
- Engage human-centered design research methods and systems thinking to identify and understand values, goals, motivations of intended audiences as a mode of inquiry, question framing and guide to action.
- Develop a high level of craft and technical skills in a relevant range of media and tools and effectively weigh applicability for intended audiences and outcomes.
- Develop and realize intent, concept and content with awareness of context and consequence.
- Implement visual patterns incorporating text, image, diagram including temporal and spatial representations to recognize, categorize, and articulate significant form and meaning
- Employ and embody ethical practices, team and cross-disciplinary collaboration, and effective communication and presentation skills.
- Apply relevant communication theories and principles and appreciate the pervasive and long-term impact of design decisions on people and societies.
- Graphic and Information Design learning outcomes
- Integrate verbal and visual content in a way that is complementary, not redundant, to construct complex visual/verbal messages.
- Utilize information and nomenclature systems, organizational grids, hierarchy, and sequence to offer audiences access to complex topics and sense making.
- Discern the ethical implications of subjective vs. objective design, and demonstrate ability to construct content along the persuasive/informative continuum according to the needs of an audience, expectations of a client, or self-initiative.